Dansehallerne to move to Kedelhuset / The Boiler House in Carlsbergbyen
/A major industrial building - part of the old Carlsberg Brewery in Copenhagen - is to become an international centre for dance.
Kedelhuset - The Boiler House - was designed by Carl Harild (1868-1932) and was completed in 1928 to supply steam and hot water for the brewery.
Carl Harild had been a pupil of Hack Kampmann and he succeeded Kampmann as architect at both the Ny Carlsberg Glyptotekk and at Carlsberg Brewery on Kampmann's death in 1920.
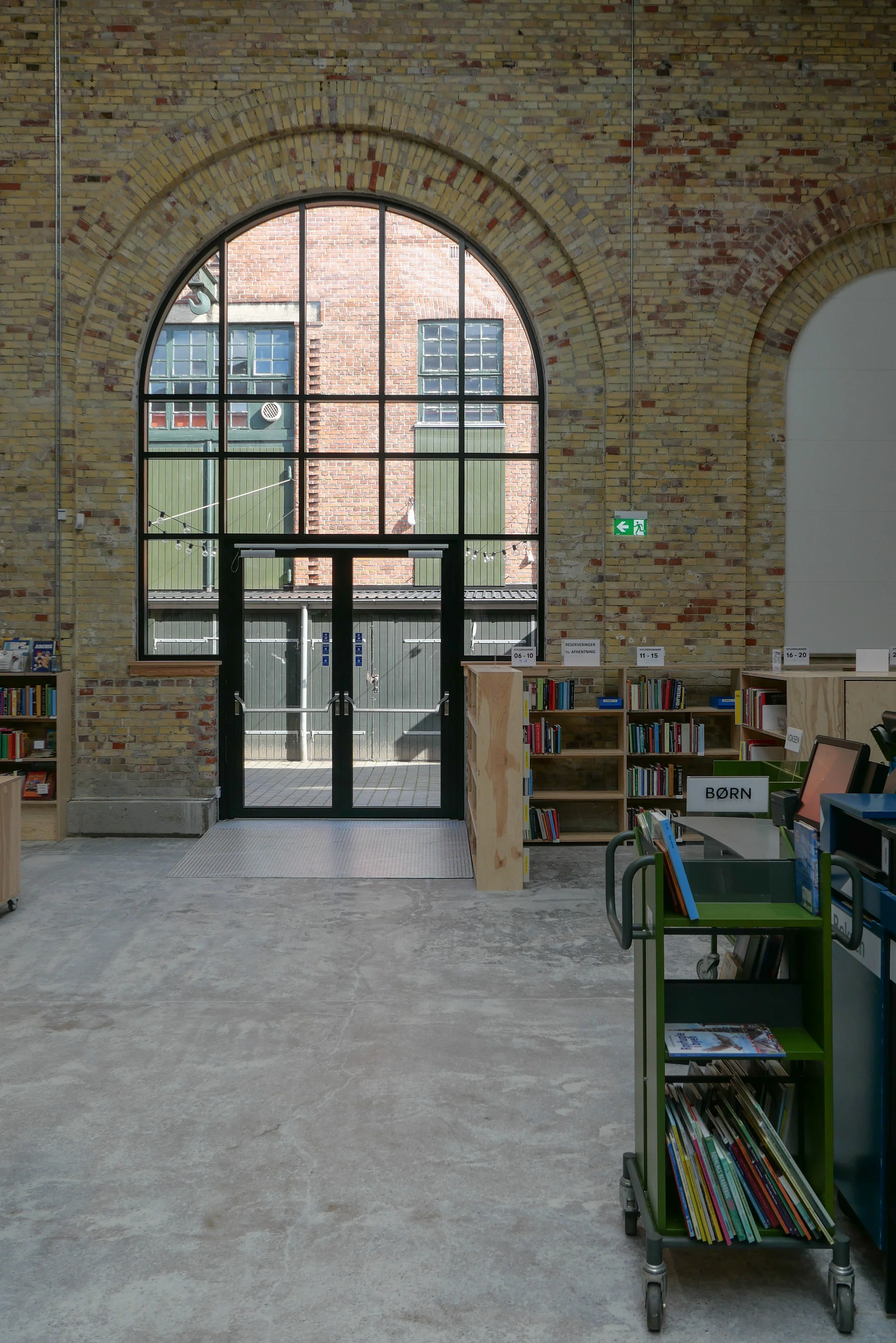
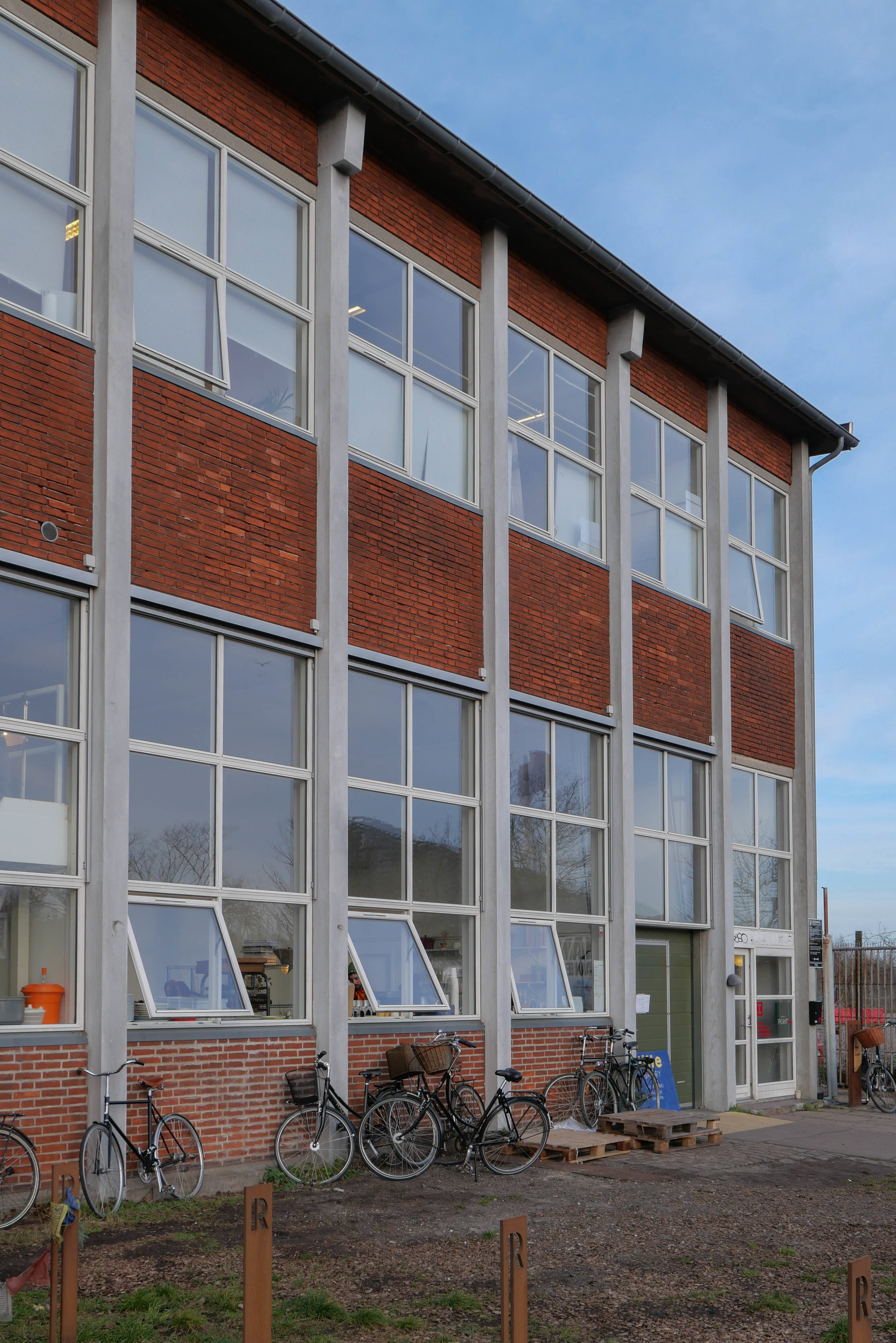
The Boiler House is a massive and impressive building at the centre of the brewery site. It is faced in red brick with a series of deep arches at the street level, with tall narrow windows at the main level and small square windows above that. Perhaps the most striking feature of the exterior are four large chimneys for the boilers on the south side.
Both Kampmann and Harild were proponents of the architectural style that is known as Nordic Classicism and features of classical architecture are obvious in the Boiler House with the careful use of symmetry and a plain stripped-back style with little decoration but architecture that relied on strong features and the use of classical forms such as lunettes and well-proportioned panelled doors and windows that are regularly divided with simple glazing bars and plain glass.
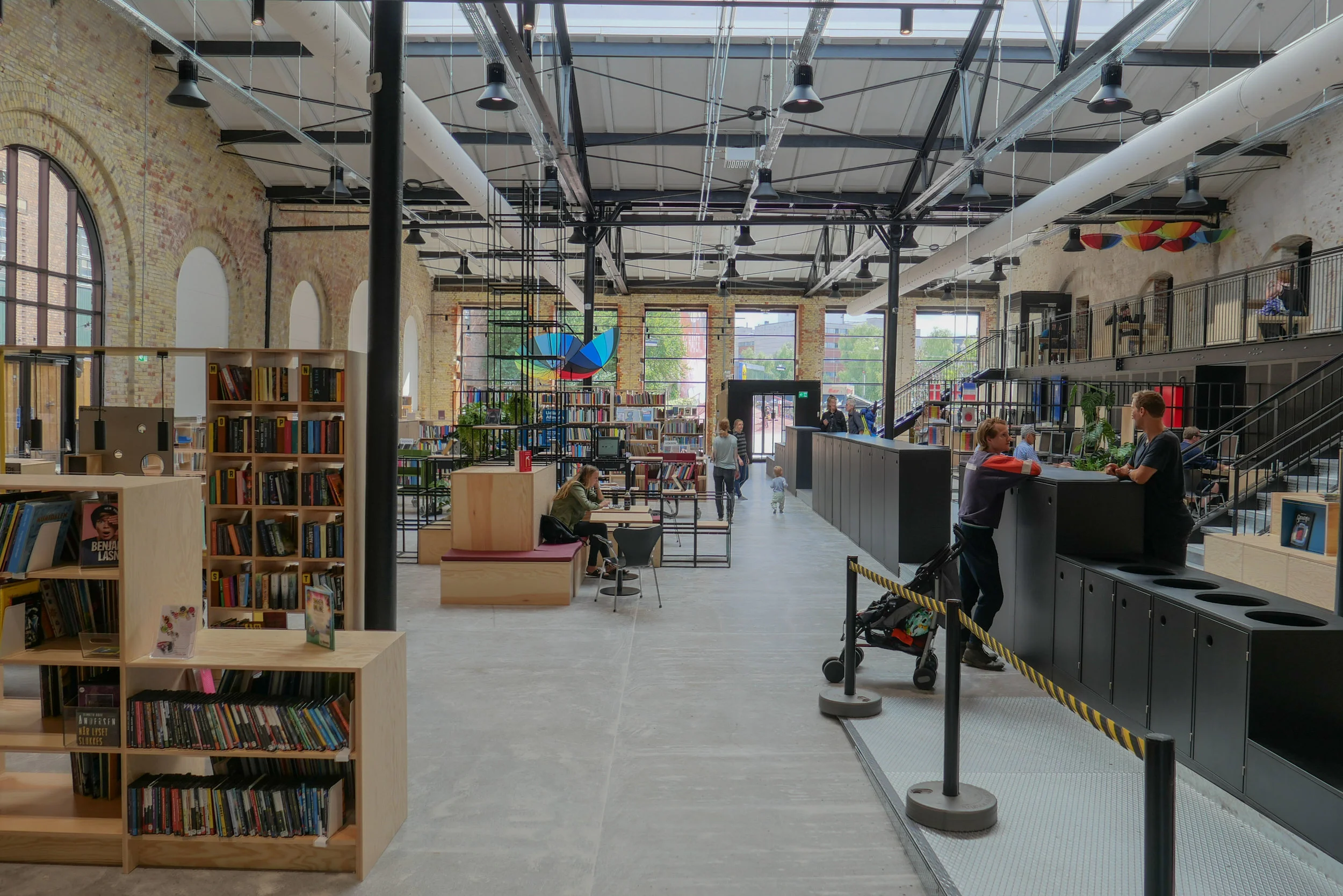
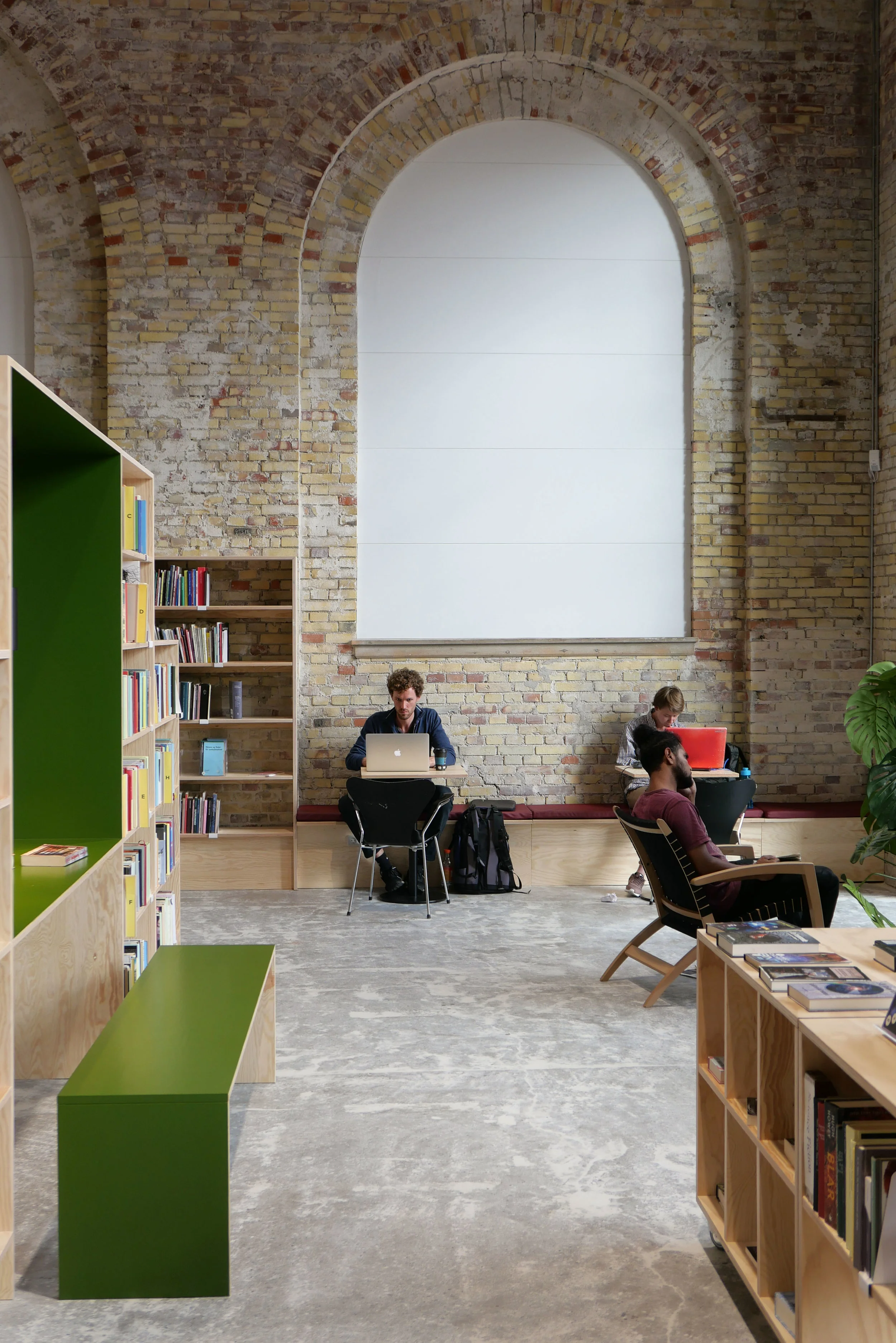
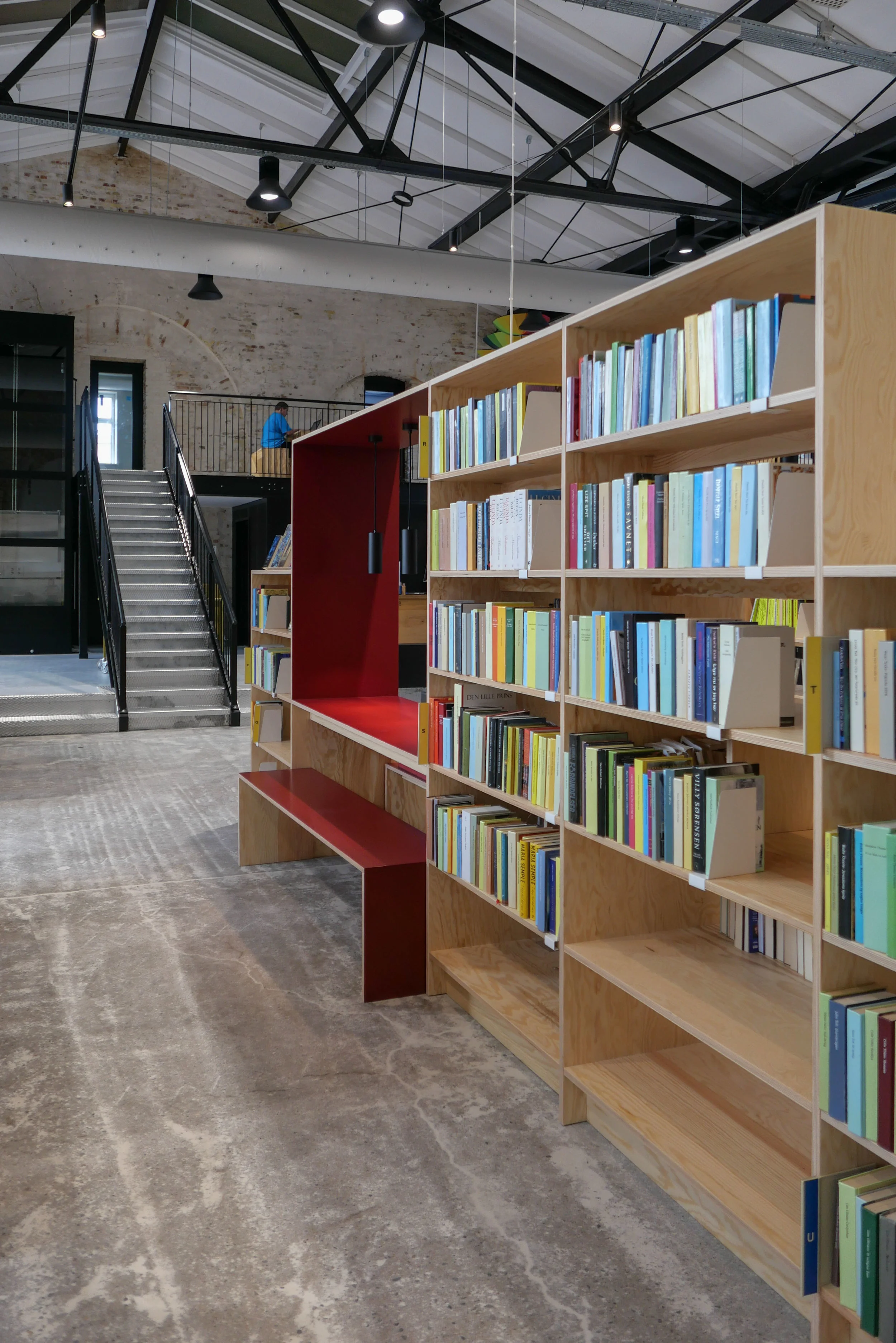
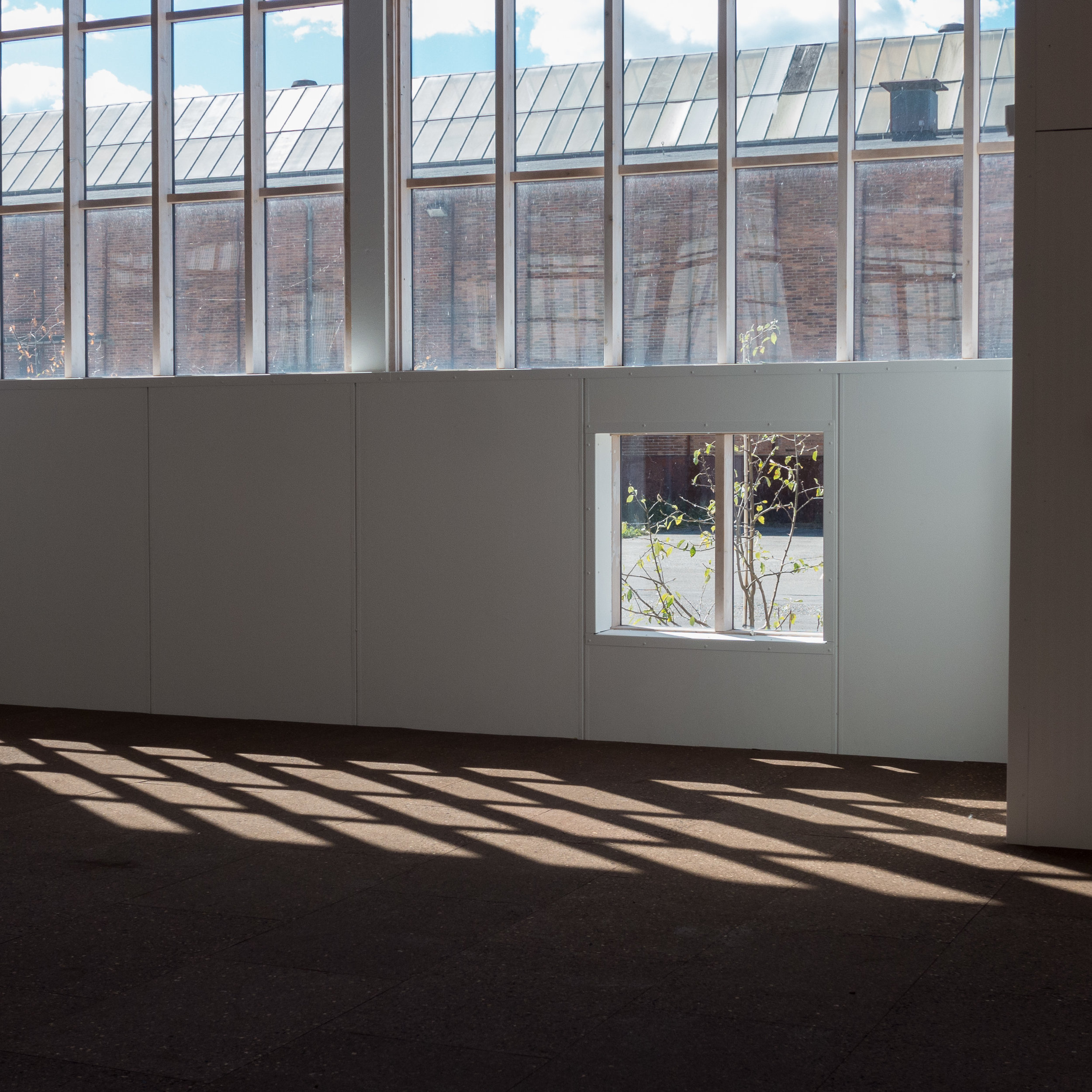
It is the interior of the building that is most dramatic with bold engineering for what is, after all, is an industrial space. There are huge concrete arches in pairs that support an impressive roof with raised lantern with glazing for top lighting down the length of the main space.
Boilers and pipework have been stripped out and the space of the main hall is now to be adapted to be a new centre for dance and performing arts for Dansehallerne. The building will include a large performance space with different possible configurations of seating as well as rehearsal areas and meeting rooms to create flexible space that can be used for performances, dance festivals, talks and training.
Dansehallerne is a national and international organisation for dance and choreography that was established in 2012 when Dansens Hus and Dansescenen merged. They were based on the Carlsberg site, at Tap E - opposite the Boiler House - but moved from there in 2017 when development of the brewery site started and they are currently based on HC Andersens Boulevard.
Mikkelsen Arkitekter AS are the architects for this major project that has financial support from the AP Møller Foundation.