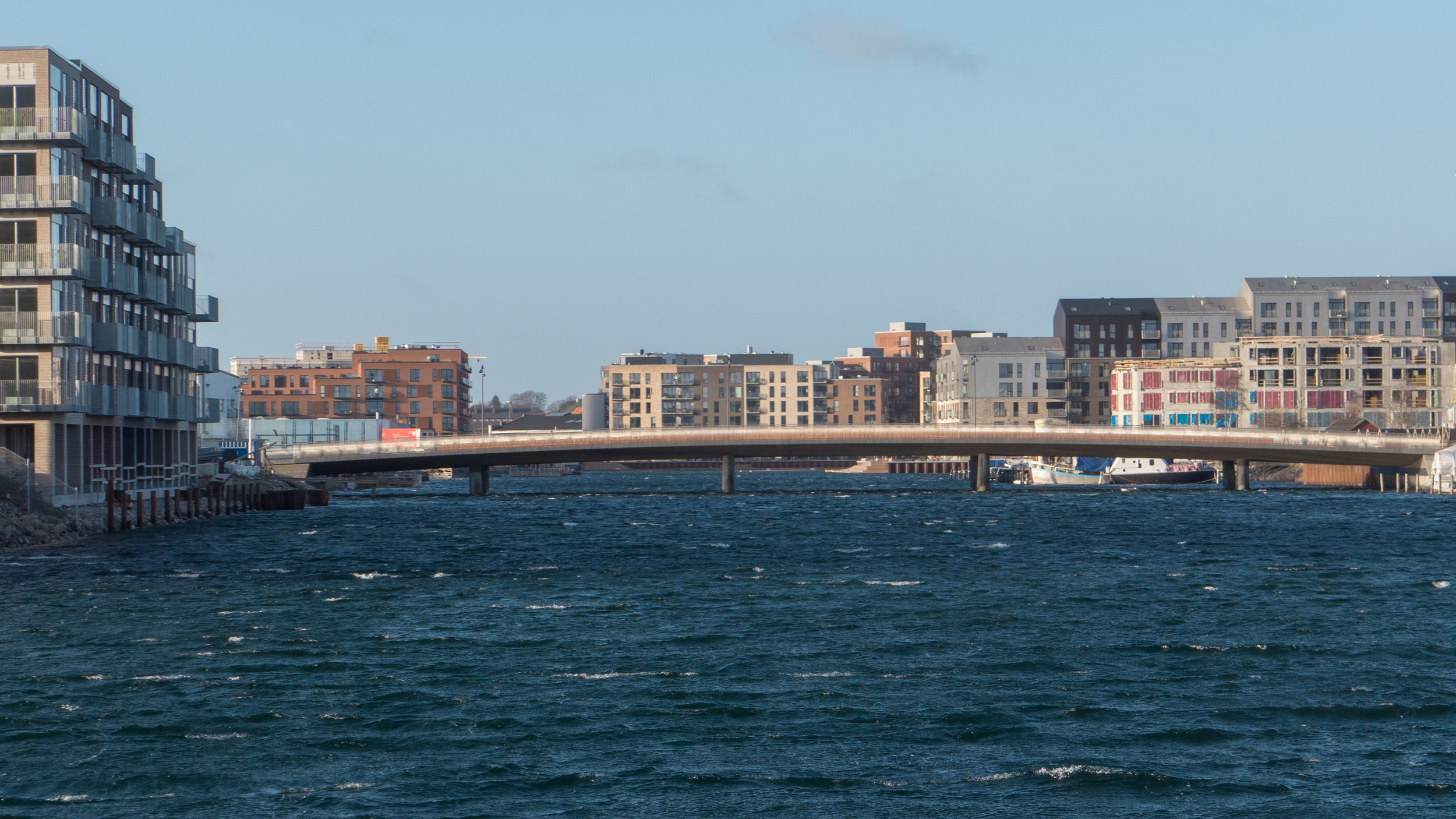
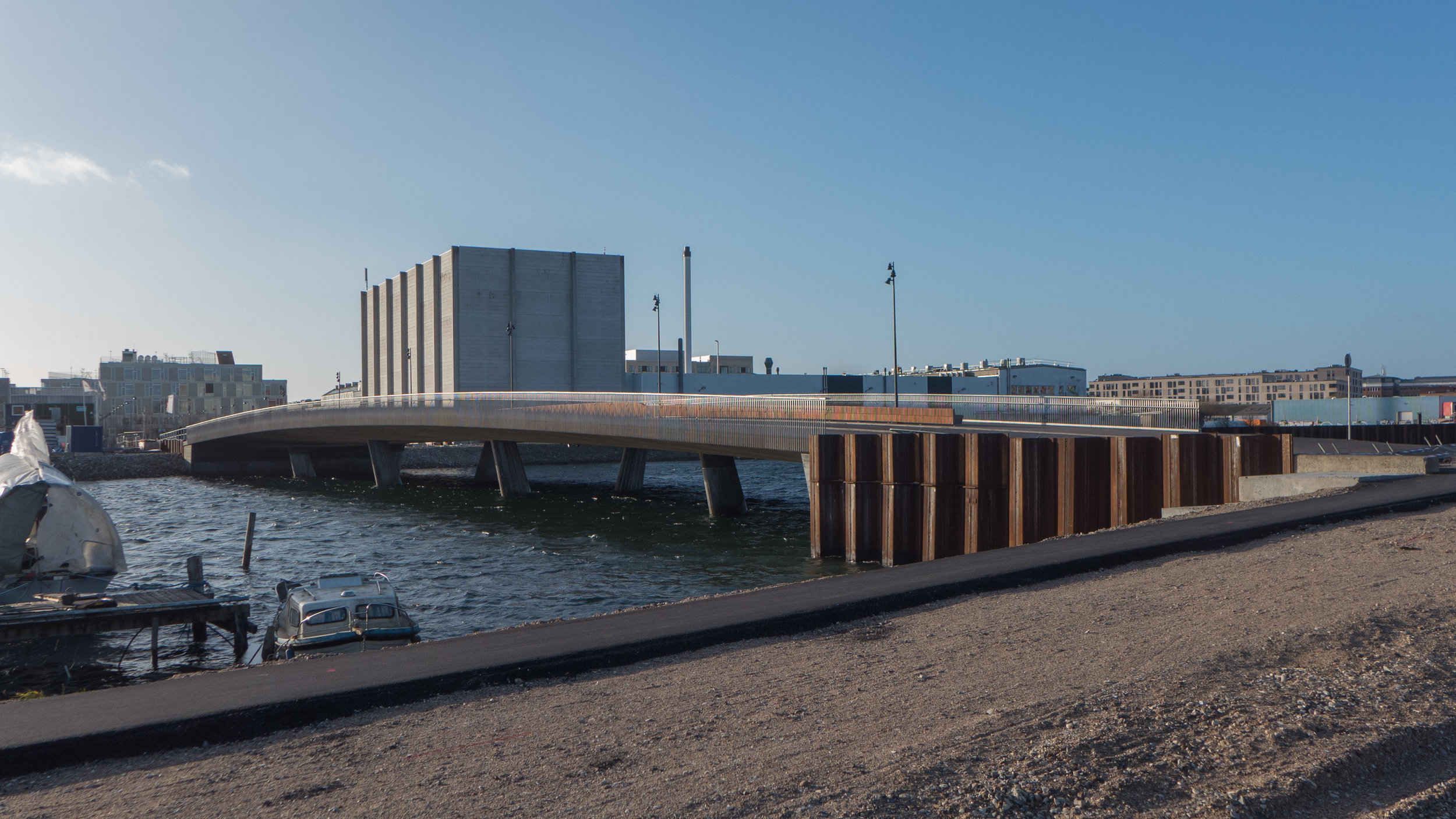
Orientkaj
/The large building to the east of the new metro station at Orientkaj - on the north side of the dock - is the new Copenhagen International School designed by CF Møller and completed in 2017. The scheme for swimming and water sport facilities is also by CF Møller.
When the first stage of new metro line M4 out to Nordhavn opens then the trains will leave the circle line at Østerport and head out towards the harbour and, after a new station at Nordhavn, will climb up onto elevated track and a new station at Orientkaj.
Here, as the trains pull into the station, to the right, looking east towards the sound, there will be a view down one of the largest docks in this part of the harbour with a line of large brick and concrete warehouses along Orientkaj itself … most dating from the second half of the last century and most bonded warehouses. These face across the dock to the new Copenhagen International School designed by CF Møller and completed in 2017.
CF Møller have designed a scheme for the dock itself with a series of islands and boarded walkways in front of the school for swimming areas, an area for water sports, - including kayak polo - and changing rooms and a sauna with facilities to be used by the school but also by the local community.
The impressive scale of the dock will be broken and the area takes another step away from its immediate past with nearly all evidence for the container port - the very reason the dock is here - lost but, and again it is a big but, it is schemes like this that will bring at least some nature back down to the quay side and will make the water a strong part of life in this area rather than simply a dramatic backdrop.