the green line continues through Nexus by Arkitema
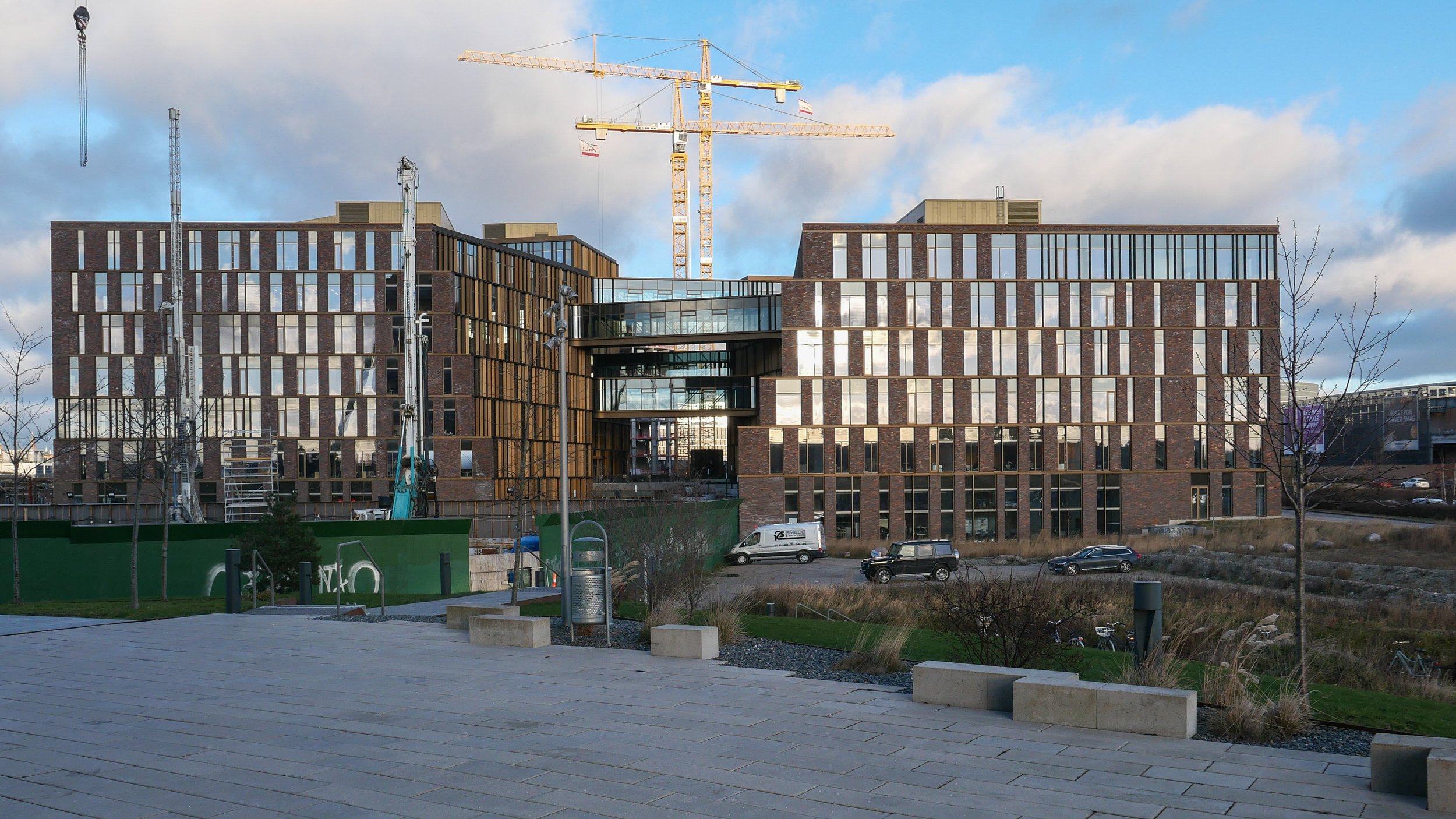
/Nexus is a large, new building where there are offices for five public agencies … Rail Net Denmark, the Danish Transport Authority, the Danish Road Directorate, the Danish Building Authority and the Danish Energy Agency.
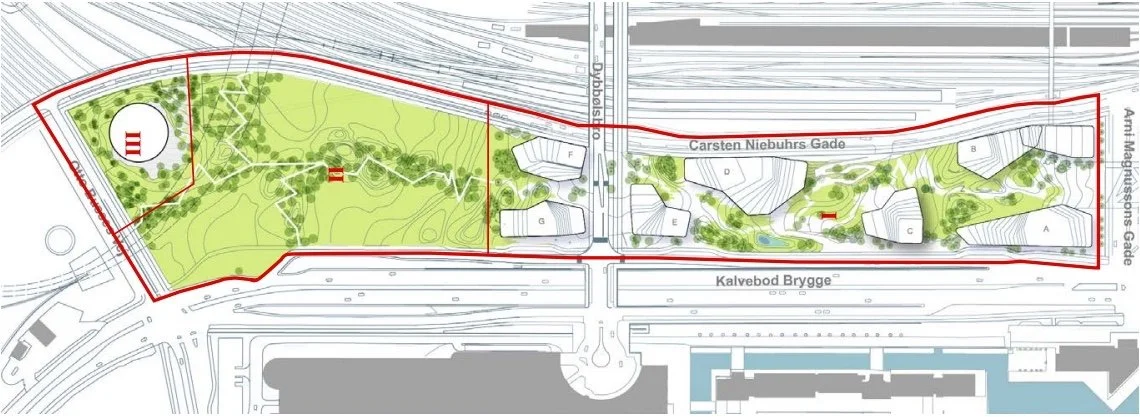
From the air view, you can see that there is a complicated, clover-leaf arrangement of four blocks and each with an atrium. From the streets around and from the central 'courtyard' this underlying arrangement is not so obvious.
There are tight, outward-facing open courtyard on both sides of the building …. so on the north side, towards the railway, there is a relatively narrow courtyard with a main entrance from the street level of Carl Niebuhrs Gade and, on the opposite side, towards Kalvebod Brygge, there is a comparable open courtyard that appears to be primarily a light well for what would otherwise be a large and deep block.
Judging by eye, the south block of the four, has two corners set at right angles - so just one side - the inner side - is set at an angle. Two blocks have a single corner each that is at a right angle - the north block with a 90 degree angle towards the small courtyard on its east side and the east block with one external right angle, towards Fisketorvet. The west block has no right angles so there appears to be a game going on here.
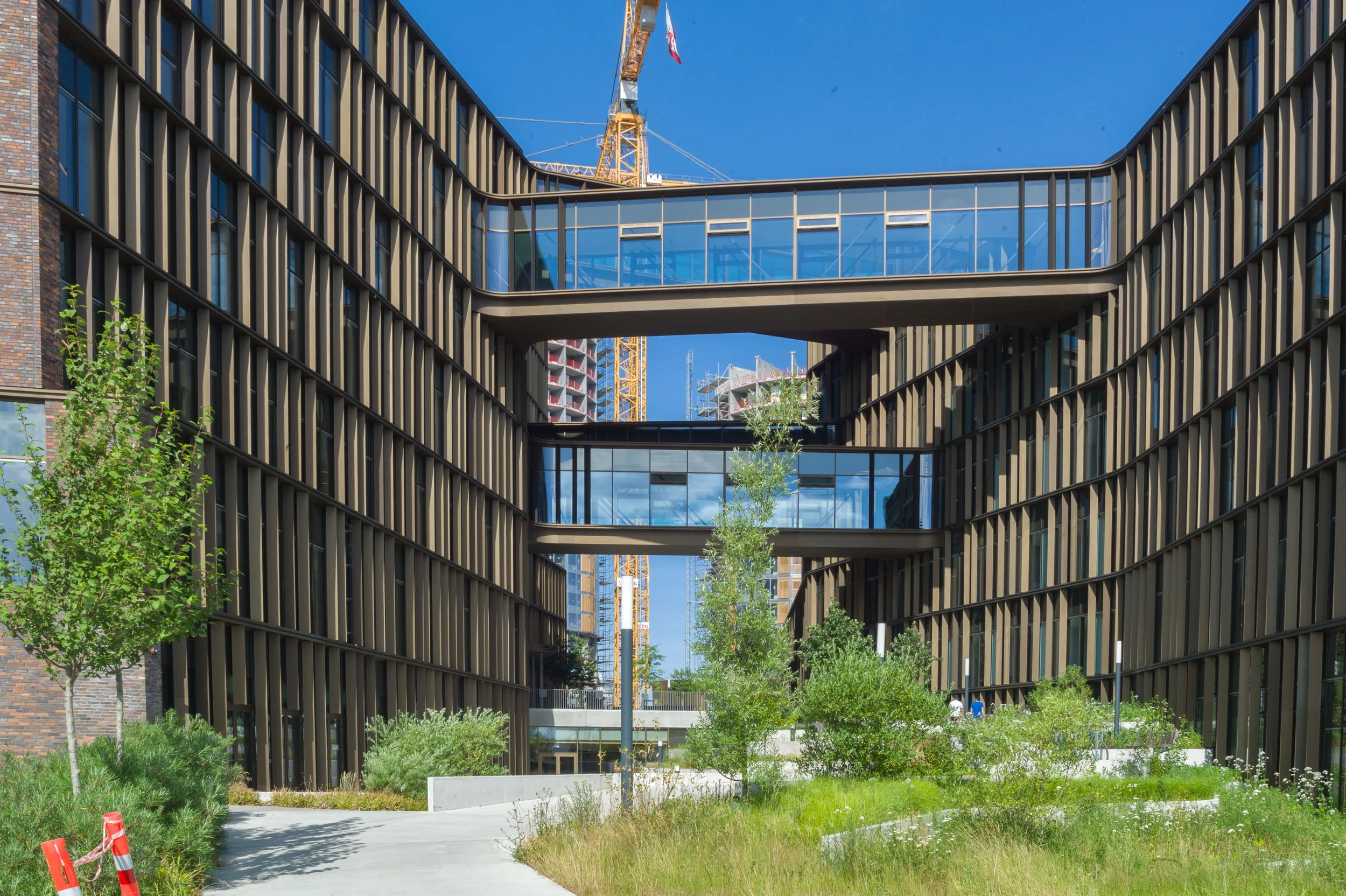
It's partly about how someone understands the relationships of the blocks from the outside as they approach the building and in part its about how the view out from the offices is guided by the angle of the external wall.
Some upper levels step back at each floor and change angle slightly so. again, it is about how the blocks are perceived and it hints, unlike a sheer wall, that the building is turning or twisting. The set backs are too small to make much difference to the shadow thrown by the building.
With the garden through the centre of the building, as part of the green line, the visitor is drawn in by the angles narrowing towards a main entrance to the offices at the upper level but also, from the entrance, the angles opening out beyond shows you the way out and on down.
This is a very sophisticated combination of angles, levels and landscape that control and direct how people see the building but also how they move around and into the building.
Inside, the atriums, staircases, wide public areas and views out to courtyards and so on all suggest a flexible work environment and is very much about people move around even during the working day. This is a stark contrast to 'modern' Danish office buildings of the 1950s and 1960s like Søllerød Town Hall by Arne Jacobsen where the over-riding arrangement in the office building is a spine corridor with single-cell work spaces on either side and that is repeated on each floor.
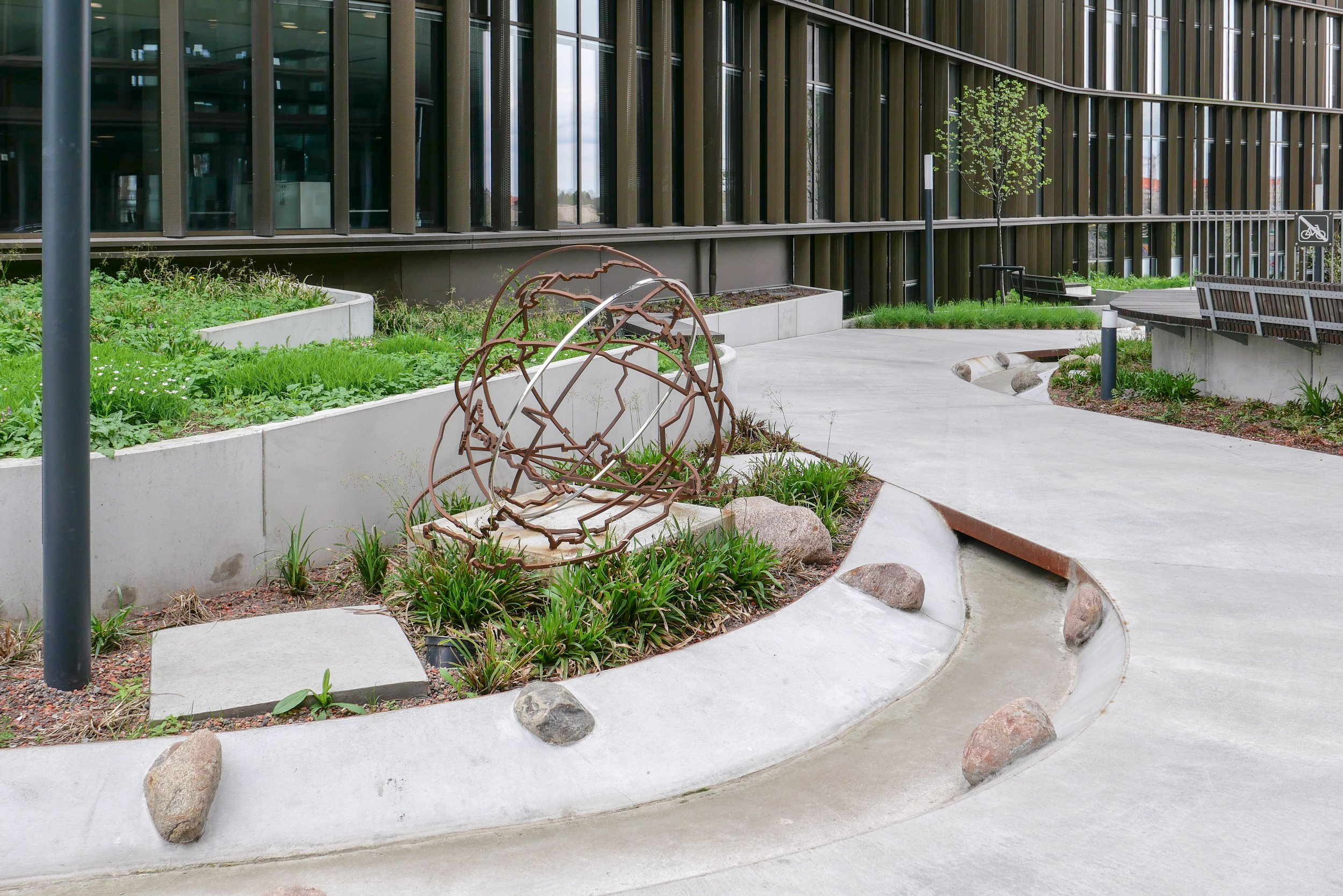
The landscape of Det Grønne Strøg - the green line - runs through the centre of the building and reads as a steeply sloping green canyon that is quite enclosed with bridges across at upper levels
Workers and visitors coming from either Dybbølsbro and the suburban train station or by bike over the cycle bridge, coming from Islands Brygge, arrive at the top of the green street on the north side and there is a main entrance there but with views down the green landscape that drops down a series of zig-zag concrete paths with a concrete rill that will take rain water down alongside the path.
Through the length of the green line, a key part of the design is that all rain water is captured and reused for the plants and trees.
New planting is attractive but, until it becomes more established, it is difficult to judge but there is a good view down from the top to the new railway control tower beyond.